IIT Madras Researchers patent ‘Combined Power Generation Technology’
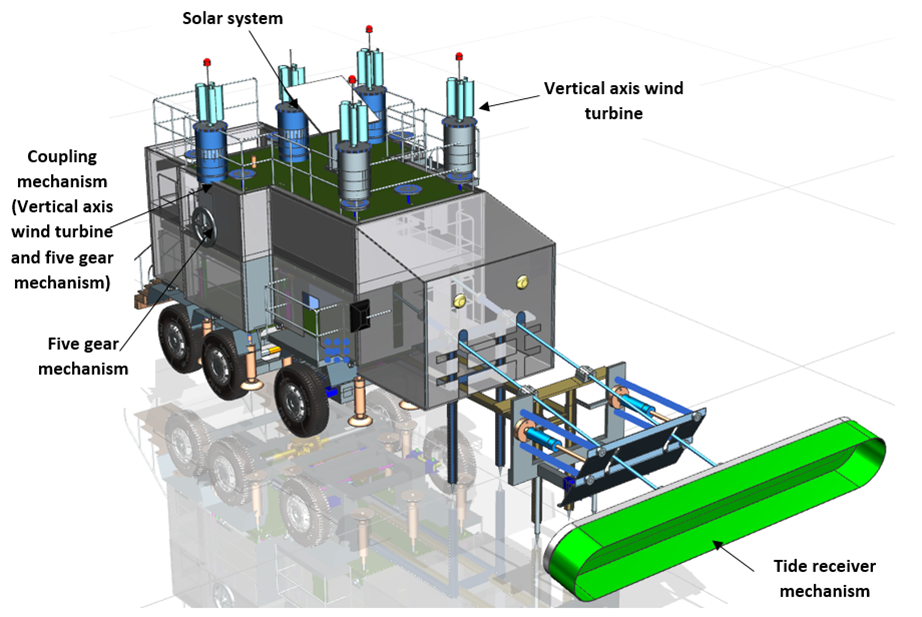
IIT Madras researchers have patented a ‘Combined Power Generation Technology’ technology that can generate electricity from both Tidal and Wind sources.
This can be deployed as a mobile vehicle For power generation, transmission and storage. The current innovation is an energy converter system that generates electricity in coastal areas to reduce electricity demand, say IIT Madras researchers.


Turbine
A wind turbine mounted on a vehicle’s roof will employ the converter technology to generate wind energy as well as convert tidal energy into electrical energy, say IIT Madras researchers.
The energy output of the system or gadget is entirely renewable and sustainable. The roof-mounted solar panel could also be used to power other equipment on mobile vehicles, say IIT Madras researchers.
Researchers team
This research was undertaken by Mr. Sadham Usean Ramasamy, PhD Research Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras, and Prof. A. Seshadri Sekhar, a former Head, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras, who is currently on deputation to IIT Palakkad as its Director.

Initially, Mr. Sadham Usean Ramasamy joined under (late) Prof. BVSSS Prasad for his PhD by Jan 2020. Currently, He is working under the guidance’s of Prof. Shilgram Tiwari and Prof. Shyama Prasad Das through the ANSYS Fellowship.
IIT Madras researchers work key aspects
Prof. A. Seshadri Sekhar, a former Head, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras, who is currently on deputation to IIT Palakkad spoke about key aspects of the work of IIT Madras researchers.
He said the current invention creates electricity using only one vertical axis wind turbine, a horizontal converter mechanism, and no hydraulic set generator based on pendulum support.

The current converter also has a variety of height adjustable guider support mechanisms to help regulate the height of the elliptical plate attached to the main shaft, he said speaking about work done by IIT Madras researchers.
The current idea, on the other hand, lacks a horizontal axis turbine and is entirely onshore, therefore there is no severe corrosion problem.
Furthermore, the converter is a remote-controlled system that can be relocated to any position based on wave height and power generation requirements, he said speaking about work of IIT Madras researchers.

The five gear converters will help operate at least one generator and install at least one vertical axis wind turbine on the roof of a double decker vehicle, he said speaking about the work of IIT Madras researchers.
The wheel arrangement based on chain teeth/tooth profiles allows the double decker mobile vehicle to be easily relocated from one place to another, he said.
Furthermore, without the need for a submarine connection, the generated electricity can be easily delivered from the transformer.
The current idea, on the other hand, lacks a horizontal axis turbine and is entirely onshore, therefore there is no severe corrosion problem.
Furthermore, the converter is a remote-controlled system that can be relocated to any position based on wave height and power generation requirements.
The five gear converters will help operate at least one generator and install at least one vertical axis wind turbine on the roof of a double decker vehicle, he said speaking about the work of IIT Madras researchers.
The wheel arrangement based on chain teeth/tooth profiles allows the double decker mobile vehicle to be easily relocated from one place to another.
Furthermore, without the need for a submarine connection, the generated electricity can be easily delivered from the transformer, he said.
Furthermore, the current invention includes individual flywheel topologies for energy storage, which aids in the continuous spinning of the generator shaft and power production, he said.
To reduce electricity use, the current innovation is an energy converter system that creates electricity in coastal areas.
It also has fewer operating expenses, requires less maintenance, and produces clean energy. It can also be used as a moving vehicle, he said.
Tidal energy is a clean, sustainable energy source with significant potential and the unusual capacity to be totally predictable.
Depending on the power demand in the coastal area, the converter system may need to be relocated, he said speaking about the work of IIT Madras researchers.
The converter technology is used by a wind turbine mounted on the vehicle’s top to create wind energy as well as convert tidal energy into electrical energy.

Furthermore, it has lower costs, requires less maintenance, and provides clean energy. It can also function as a mobile vehicle. Tidal energy is a clean, sustainable energy source with a lot of potential and the uncommon ability to be completely predictable, he said speaking about work of IIT Madras researchers.
The converter system may need to be relocated depending on the power demand in the coastal area. The system’s or gadget’s energy output is fully renewable, he said.
The solar panel on the roof is also used to power other equipment on mobile vehicles. The converter system may need to be relocated depending on the power demand in the coastal area, he said speaking about the work of IIT Madras researchers.
Novelty
The following mechanisms are unique to the current technology and have specialised features: spring-assisted mechanism, adjustable guider structural support mechanism, main shaft with five converter gear shaft mechanisms, direction converter gear mechanism, floor level adjustable mechanism, and gear coupling mechanism, say IIT Madras researchers.
Highlighting novel aspects of work of IIT Madras researchers Sadham Usean Ramasamy, PhD Research Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras, said this technology will potentially entail fewer expenditures, require less maintenance and produce clean and sustainable energy.
‘It can also be utilised as a mobile vehicle. With a lot of potential and the rare capacity to be entirely predictable, tidal energy is a clean, sustainable energy source.’
The Potential Industry partners of this technology include companies in the Power sector, Solar and Wind Energy, he said.
Five systems
This technology consists of five systems that aid in the conversion of wind and tide energy into electrical energy. To transform tide energy into electrical energy, the converter system employs a one-of-a-kind five-gear mechanism, say IIT Madras researchers.
To help convert tidal and wind energy into electrical energy, spring-assisted mechanisms, adjustable guider structural support mechanisms, main shaft with five converter gear shaft mechanisms, direction converter gear mechanism, floor level adjustable mechanism, and gear coupling mechanism are used, say IIT Madras researchers.
Additionally, the solar panel on the roof is used to power other systems on mobile vehicles, say IIT Madras researchers.

Tidal energy has the potential to be used to generate electricity in the future, despite the fact that it is not now widely utilized. As a resource, ocean energy is essentially untapped, say IIT Madras researchers.
The current technology focuses on combined power generation, which employs both tidal and wind energy to generate electricity.
The technology developed by IIT Madras researchers envisages locating the entire converter onshore. Hence, there would be no major corrosion issues.
Additionally, the converter is a remote-based system that can be moved to any location based on wave height as well as power generation requirements, say IIT Madras researchers.
S Vishnu Sharmaa now works with collegechalo.com in the news team. His work involves writing articles related to the education sector in India with a keen focus on higher education issues. Journalism has always been a passion for him. He has more than 10 years of enriching experience with various media organizations like Eenadu, Webdunia, News Today, Infodea. He also has a strong interest in writing about defence and railway related issues.






